
by Joe Bunting |
How do good stories start? In the middle of the action? With a slow buildup to the action?
Exposition is a literary term that deals with how to start a story.
In this article, I’ll define exposition, talk about how it fits into the dramatic structure, give examples of expositions from popular novels, plays, and films, and then give a few tips on how to use the exposition best in your writing.

by Sarah Gribble |
Horror is a genre of literature or film that wants to evoke fear, shock, and suspense. Characters battle for their life versus a fate worse than death.
What makes a good horror story is the ability to tap into our deepest fears and deliver them in a captivating way. Even if you don’t consider yourself a horror writer, practicing a few short stories in this genre can help you understand human fear and the way it motivates action.

by J. D. Edwin |
Finishing a first draft is a huge deal. If you just accomplished this, be proud of yourself! At the same time, you might be wondering how to revise a novel after that first draft is done. There’s a lot of advice out there. Which do you listen to?
The revision process doesn’t have to be complicated. However, you might feel—especially if this is your first completed draft ever—intimidated to edit your book. There’s a lot of words and scenes to review. Where do you begin?
In this article, I’d like to share how I took a daunting editing process and created a simplified, concise, and clear strategy to revising your first draft. I do this with what I call a Revision List—a table with five columns that can help you simplify big ideas.
If you’re like me, you won’t ever want to edit a first draft without it!
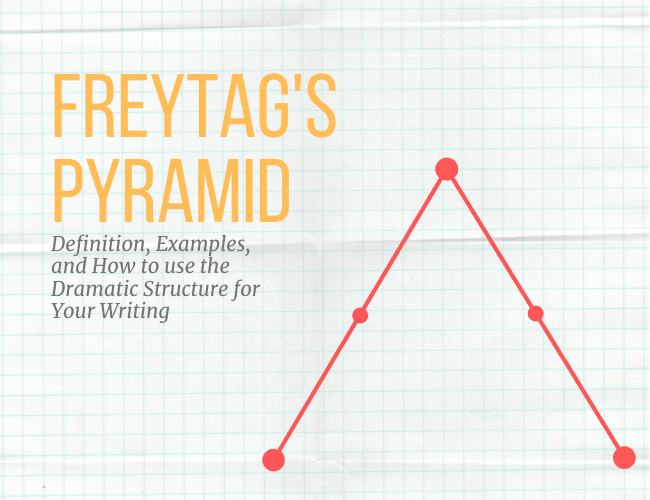
by Joe Bunting |
Most great stories, whether they are a Pixar film or a novel by your favorite author, follow a certain dramatic structure.
When you’re getting started with writing, understanding how the structure works is difficult. Even if you go back and analyze your favorite books and films, it can still be hard to structure your own stories. That’s where Freytag’s Pyramid can help.

by David Safford |
In this story type, the hero and their comrades are attempting to thwart death in the face of an overwhelming physical obstacle, usually in the form of a figure of nature.
This isn’t to say that an adventure story can’t have a villain. However, the primary threats will always come in physical form, forcing the characters to dig deep and find the strength and resolve to endure.

by Joe Bunting |
We often think that to create conflict we need to show spectacular events. For example, a car chase, an argument between lovers, a fistfight, or the threat of a nuclear explosion. Or we think of conflict as some kind of internal suffering: depression, longing, or pain.
But the truth is that if events and emotions were the only elements of conflict in our stories, we’d have some pretty flat stories.
Conflict, in good stories, is not about spectacular events or painful emotions. Good conflict is about values.








